Windows 365 is a service that provides a Windows Cloud experience, allowing users to access a Windows desktop from anywhere. I talked about this before in my Windows 365: Zero to Cloud in 1 hour!– article. One of the key features of Windows 365 is the ability to create restore points, which are snapshots of the system at a specific point in time. Let’s take a look at what those mean!
Overview of Windows 365 Restore Points
Using restore points in Windows 365 offers several advantages. Firstly, they provide a safety net for system recovery, ensuring that users can quickly restore their system to a working state in case of any issues.
Secondly, restore points help protect data by preserving user settings and installed applications. This means that even if a system crash occurs, users can recover their data without losing important information.
Additionally, restore points can be used to test new software or updates, allowing users to revert to a previous state if the changes cause problems.
How to adapt the automatic Windows 365 Restore Points in Microsoft Intune
By default Microsoft Intune will create several restore points for each and every Cloud PC.
The amount of restore points will never change and is two bi-weekly restore points and ten restore points you can adapt the recurrence of, this is done through a “User Setting”:
Once you are here, you can adapt the recurrence.
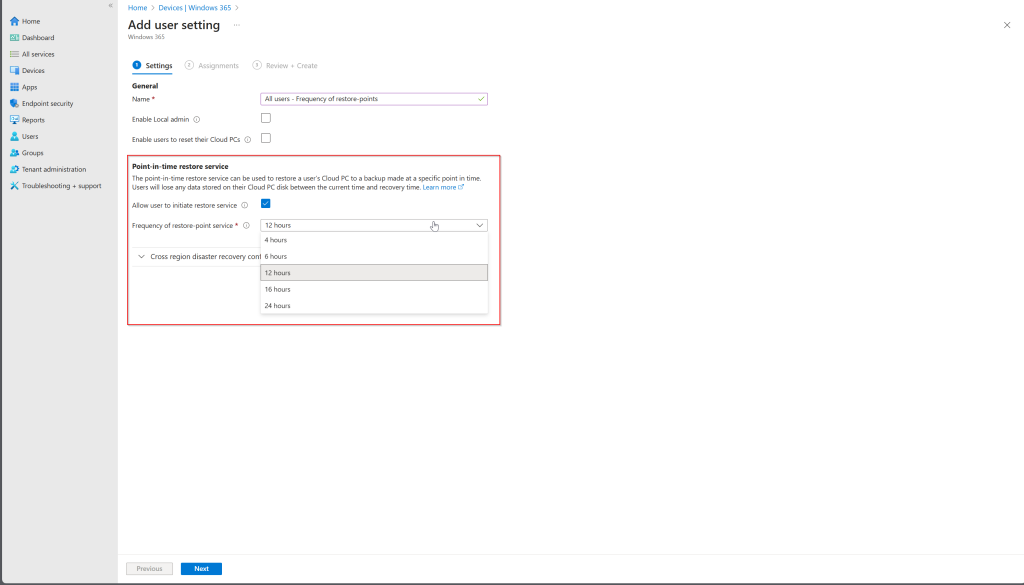
What about Storage Accounts?
Storage accounts play a crucial role in managing restore points for Windows 365. These provide a secure solution for storing large amounts of data, including your restore points.
By utilizing storage accounts, users can ensure that their restore points are safely stored and easily accessible when needed. One of the key benefits of using storage accounts is the ability to manage data efficiently, with options for redundancy and backup to protect against data loss.
Additionally, storage accounts offer flexibility, allowing users to configure permissions and access controls to suit their needs. To use storage accounts for restore points, users can integrate their Windows 365 environment with Azure, setting up containers and blobs to store the restore points securely.
This integration ensures that restore points are preserved long-term and can be retrieved quickly in case of system recovery needs.
Creating the right Azure Storage Account
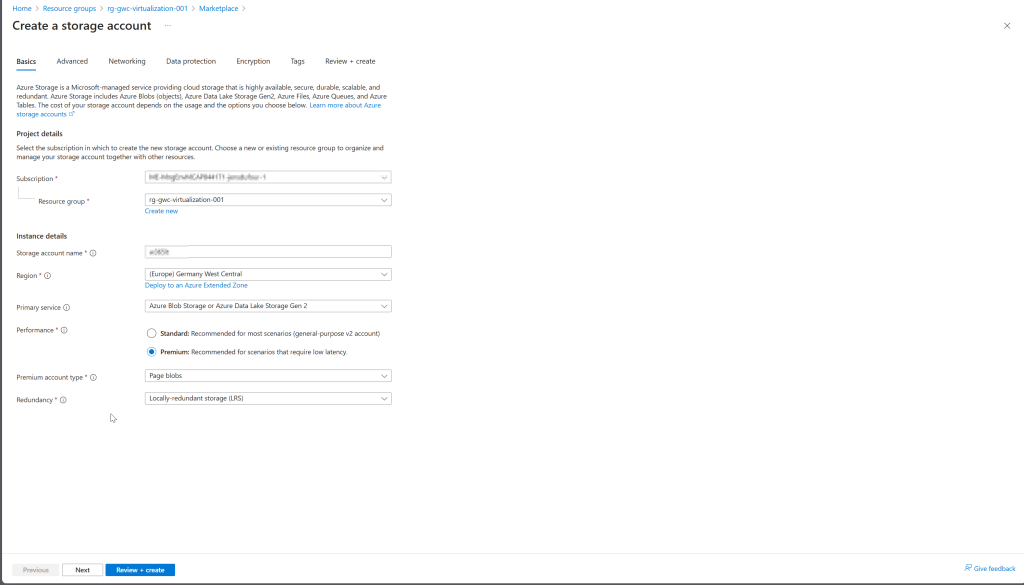
There a few requirements to be met when creating a Storage Account for the Restore Points of the Cloud PC. They are listed below and we will go over the steps needed in Azure after these.
- Instance details
- Region: Same region as Cloud PC is recommended because of performance. There is no restriction on which region you should choose.
- Performance: Premium (supports hot access tier) or Standard (supports all access tiers).
- Premium account type: Page blobs
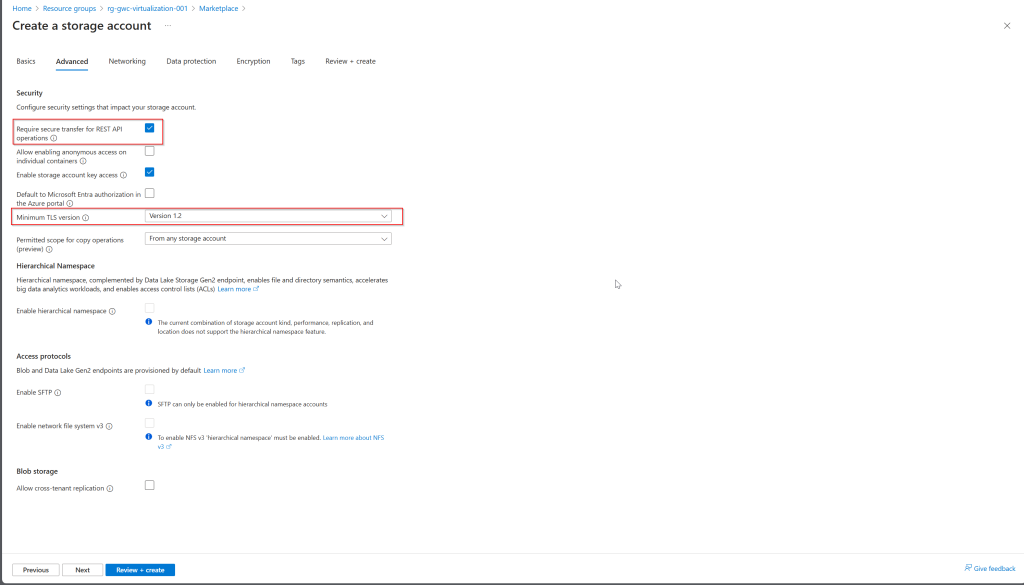
- Security
- Minimum TLS version: Version 1.2.
- Confirm Allow blob anonymous access is disabled (the default).
- Disable Enable storage account key access.
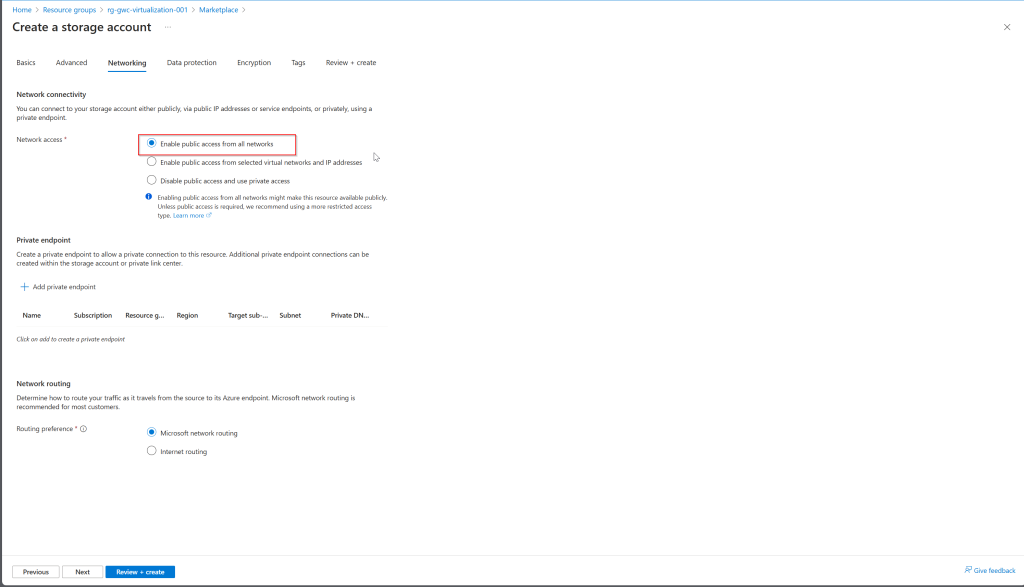
- Networking
- Network access: Enable public access from all networks
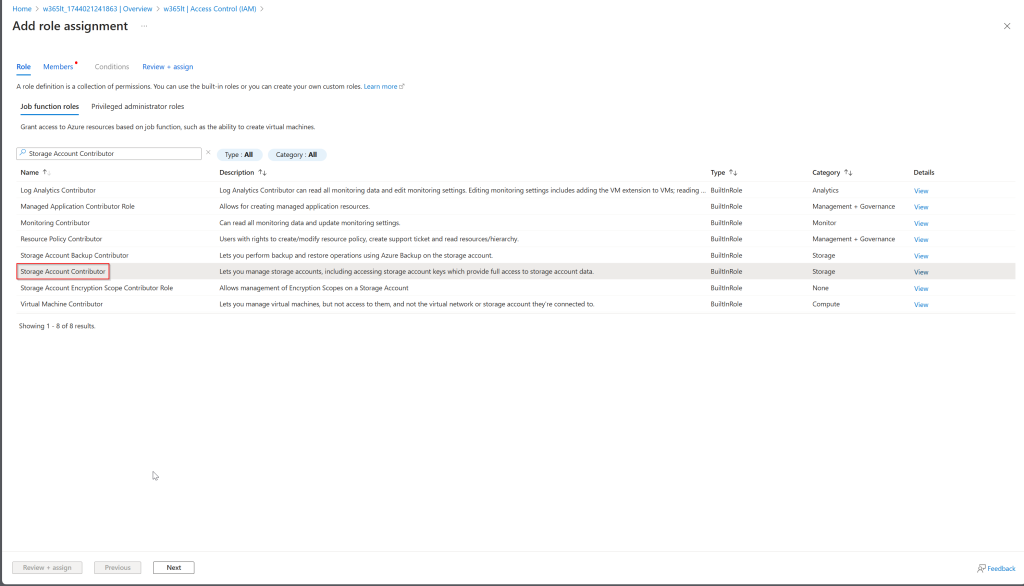
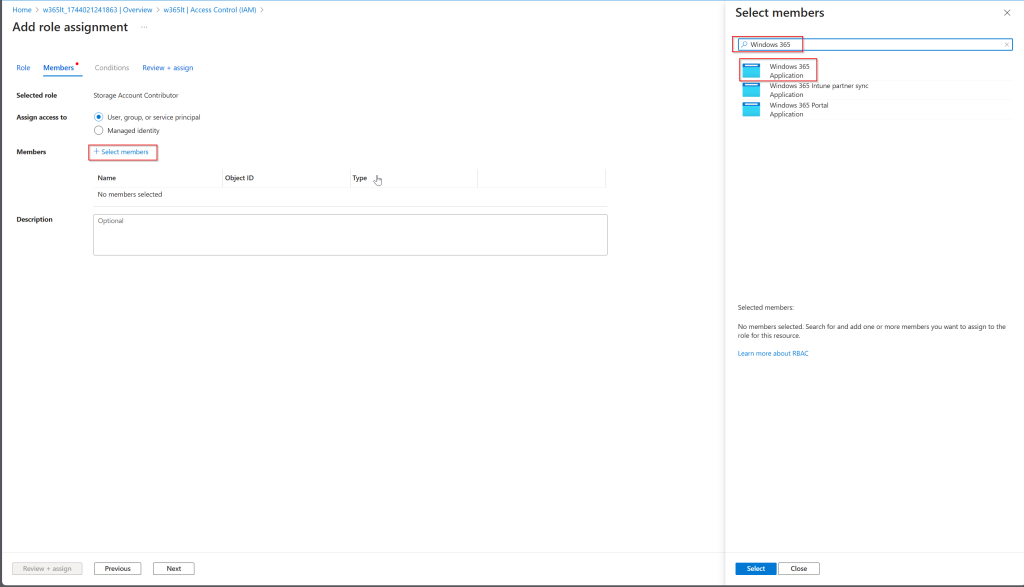
Creating a manual Restore Point in Microsoft Intune
Once the Storage Account has been set up, you have the option to create a manual restore point in Microsoft Intune.
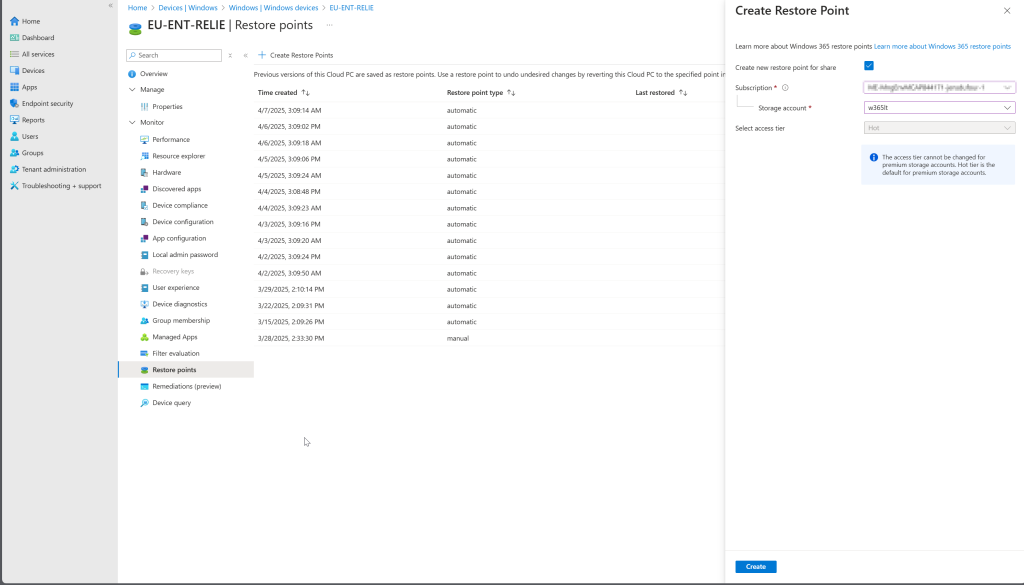
If this option is not visible, verify the requirements above as the Storage Account will not be visible if it does not meet these.
Conclusion
In summary, Windows 365 restore points are an essential feature. They provide a reliable way to recover from system issues, preserve user settings, and test new software or updates.
By creating and managing restore points effectively, users can safeguard their systems and minimize downtime.
Additionally, utilizing storage accounts for long-term storage of restore points offers a scalable and secure solution for preserving these critical backups. I encourage everyone to take advantage of them in Windows 365 to enhance system management and data protection strategies.